PMI-ACP certification exam overview
PMI-ACP certification exam overview
The PMI-ACP certification is intended for practitioners who work on Agile project teams but not just project managers.
The PMI-ACP certification :
• Measures a practitioner’s knowledge and skill in Agile principles, practices, tools, and techniques
• Covers multiple Agile methodologies
• Intended to cover use of Agile both in Information and Communications Technology (ICT) and outside
ICT
The Value of PMI-ACP ® :
• For practitioners, PMI-ACP ® helps:
o Demonstrate a level of professionalism in Agile principles, practices, tools and techniques
o Increase professional versatility in project management
• For organizations, PMI-ACP ® demonstrates a practitioner’s:
o Knowledge of Agile practices, which shows the practitioner has greater breadth and depth as a PM
PMI-ACP – Eligibility Requirements
Requirement Description : Educational Level Secondary degree (high school or equivalent) or higher
General Project
Experience : 2,000 hours working on project teams. These hours must be earned within the last 5 years. Note: a PMP will be accepted to fulfill these requirements.
Agile Experience : 1,500 hours working on Agile project teams. These hours are in addition to the 2,000 general practice hours. These hours must be earned within the last 3 years.
Agile Training : 21 contact hours; hours must be earned in Agile project management topics
Examination Tests knowledge of Agile fundamentals and ability to apply to basic projects
Maintenance : 30 PDUs/3 CEUs every 3 years in Agile project management
Note: hours would count toward PMP
Cost : $435 PMI member; $495 PMI non-member
The process :
Complete certification application
Submit certification application /
Initial review of application
Pay certification fee
Audit (if selected) of education
and experience documentation
Take examination / assessments
Exam Design Objectives
Test Agile project knowledge and application:
• Most projects
• Most of the time
• Some remote team members
Not another Scrum (or XP, FDD) exam
• Combines Agile, Lean, and Kanban
Meet Agile Alliance Exam Guidance
“…employers should have confidence only in certifications that are skill-based and difficult to achieve.”
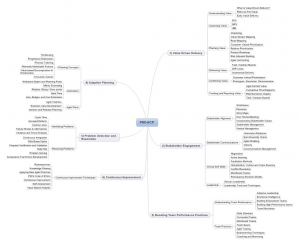
Exam Content
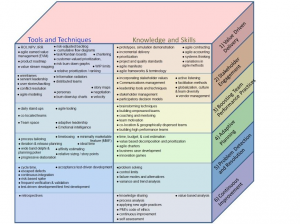
Tools & Techniques
Things you should be able to do.
The exam tests your ability to apply them, often through “do,” “calculate,” or “identify what happens next” type questions
Knowledge & Skills
Things you should know.
The exam tests your understanding and recall of them through questions that assess the “how” and “why” of the topics being tested
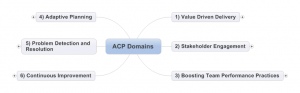
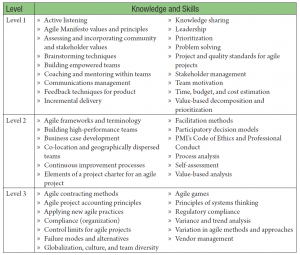
The “Tools &Techniques” and “Knowledge & Skills” Are split into 6 Domains
1) Value Driven Delivery
2) Stakeholder Engagement
3) Boosting Team Performance
4) Adaptive Planning
5) Problem Detection & Resolution
6) Continuous Improvement
Exam content outline
Tools & Techniques (50%)
Knowledge & Skills (50%)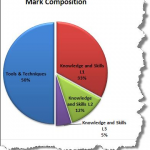
PMI ACPism’s
Be aware of Exam Question Assumptions:
• Assume a small, dedicated team (7 plus or minus 2) rather than a large one
• Delivery Team includes scrum master BA, QA, developer, product owner
• Collaboration is always better than command control style management
• Face-to-face (co-location) is better than virtual
• A stable team establishes a predictable velocity
• Teams self-organize, self-govern, self-directed, make their own commitments
• Recognize you can’t know everything at the beginning of a project
• A software product can be delivered incrementally
• Questions are asked from the perspective of a team
• On the iron triangle, agile sets the time and cost, scope varies
• Terminology: Timebox, sprint (scrum), iteration (xp) are used interchangeably
Exam Taking Tips
1. Find the test centre ahead of time
2. Bring authorization letter & two forms of ID
3. Wear comfortable clothes
4. Bring snacks
5. You will be given scratch paper and pencils
6. Write down anything you are having trouble remembering
7. You will see one question on the screen at a time. You can answer a question and/or mark it to return to it later.
8. The exam does not adapt to your answers
9. Use deep-breathing techniques to help relax
10. Use all the exam time. Do not leave early unless you have reviewed each question twice.
11. Find the question in the question text then read the rest of the text. Determine what your answer should be, and then look at the answer options shown
12. Read all 4 choices and choose the BEST answer
13. Quickly eliminate answers that are highly implausible
14. There may be more than one “correct” answer to each question, but only one “BEST” answer
15. Watch out for choices that are true statements, but do not answer the question
16. Options that represent broad, sweeping generalizations tend to be incorrect, so be alert for “always,” “never,” “must,” “completely,” and so forth. Alternatively, choices that represent carefully qualified statements tend to be correct, so be alert for words such as “often,” “sometimes,” “perhaps,” “may,” and “generally.”
Samples Question
Questions fall into:
1. Application of Tools and Techniques
2. Recall of Knowledge and Skills
3. Situational questions
Question 1 :
“An agile team is planning the tools they will use for the project. They are debating how they should show what work is in progress. Of the following options, which tool are they most likely to select?”
A) User story backlog
B) Product roadmap
C) Task board
D) Work breakdown structure
Answer 1 : C) Task board
Question 2 :
The Agile Manifesto value “customer collaboration over contract negotiation” means
that:
A) Agile approaches encourage you not to focus too much on negotiating contracts, since most vendors are just out for themselves anyway.
B) Agile approaches focus on what we are trying to build with our vendors, rather than debating the details of contract terms.
C) Agile approaches prefer not to use contracts, unless absolutely necessary, because they hamper our ability to respond to change requests.
D) Agile approaches recommend that you only collaborate with vendors who are using agile processes themselves.
Answer 2 : B) Agile approaches focus on what we are trying to build with our vendors, rather than debating the details of contract terms.
Explanation : Valuing customer collaboration over contract negotiation means we look for mutual understanding and agreement, rather than spend our time debating the fine details of the agreement.
Question 3 :
Which of the following items is not a benefit associated with product demonstrations?
A) Learn about feature suitability
B) Learn about feature usability
C) Learn about feature estimates
D) Learn about new requirements
Answer 3 : C) Learn about feature estimates
Explanation: Product demonstrations provide the benefits of learning about feature suitability and usability, and they can prompt discussions of new requirements. They are not typically used to learn about feature estimates, however, since estimating is done during estimation sessions, rather than during demonstrations.
Question 4 :
An agile team is planning the tools they will use for the project. They are debating how they should show what work is in progress. Of the following options, which tool are they most likely to select?
A) User story backlog
B) Product roadmap
C) Task board
D) Work breakdown structure

Tasks board
Answer 4 : C) Task board
Explanation: Of the options presented, the best tool to show work in progress is a task board. The user story backlog shows what work is still remaining to be done on the project. The product roadmap shows when work is planned to be completed.
Work breakdown structures are not commonly used on agile projects.
Question 5 :
When using a Kanban board to manage work in progress, which of the following best summarizes the philosophy behind the approach?
A) It is a sign of the work being done and should be maximized to boost performance.
B) It is a sign of the work being done and should be limited to boost performance.
C) It is a sign of the work queued for quality assurance, which should not count toward velocity.
D) It is a sign of the work queued for user acceptance, which should not count toward velocity.
Answer 5 ; B) It is a sign of the work being done and should be limited to boost performance.
Explanation: A Kanban board shows work in progress (WIP), which represents work started but not completed. Therefore, the WIP should be limited and carefully managed to maximize performance. More WIP does not equal more output; in fact, it is quite often the opposite.
Question 6 :
As part of stakeholder management and understanding, the team may undertake customer persona modeling. Which of the following would a persona not represent in this context?
A) Stereotyped users
B) Real people
C) Archetypal description
D) Requirements
Answer 6 : D) Requirements
Explanation : Personas do represent real, stereotyped, composite, and fictional people. They are archetypal (exemplary) descriptions, grounded in reality, goal-oriented, specific, and relevant to generate focus. Personas are not a replacement for requirements on a project, however.
Question 7 :
Incremental delivery means that:
A) We deliver nonfunctional increments in the iteration retrospectives.
B) We release working software only after testing each increment.
C) We improve and elaborate our agile process with each increment delivered.
D) We deploy functional increments over the course of the project.
Answer 7 : D) We deploy functional increments over the course of the project.
Explanation : Incremental delivery means that we deploy functional increments over the course of the project. It does not relate to retrospectives, testing, or changes to the process, so the other options are incorrect, or “less correct”.
Question 8 :
To ensure the success of our project, in what order should we execute the work, taking into account the necessary dependencies and risk mitigation tasks?
A) The order specified by the project management office (PMO)
B) The order specified by the business representatives
C) The order specified by the project team
D) The order specified by the project architect
Answer 8 : B) The order specified by the business representatives
Explanation: It is largely the business representatives who outline the priority of the functional requirements on the project. That prioritization is then a key driver for the order in which we execute the work.
Question 9 :
When managing an agile software team, engaging the business in prioritizing the backlog is an example of:
A) Technical risk reduction
B) Incorporating stakeholder values
C) Vendor management
D) Stakeholder story mapping
Answer 9 : B) Incorporating stakeholder values
Explanation : We engage the business in prioritizing the backlog to better understand and incorporate stakeholder values. Although such engagement will likely impact technical risk reduction, vendor management, or stakeholder story mapping, these are not the main reasons we engage the business.
Question 10 :
The steps involved in value stream analysis include:
A) Create a value stream map to document delays and wasted time, such as meetings and coffee breaks.
B) Create a value stream map of the current process, identifying steps, queues, delays, and information flows.
C) Review the value stream map of the current process and compare it to the goals set forth in the project charter.
D) Review how to adjust the value stream charter to be more flexible.
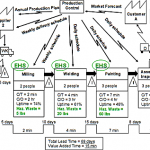
Value stream mapping
Answer 10 : B) Create a value stream map of the current process, identifying steps, queues, delays, and information flows.
Explanation : The only option here that is a step in value stream analysis is “Create a value stream map of the current process, identifying steps, queues, delays, and information
Question 11 :
What is the process cycle efficiency of a 2-hour meeting if it took you 2 minutes to schedule the meeting in the online calendar tool and 8 minutes to write the agenda and e-mail it to participants?
A) 90%
B) 8%
C) 92%
D) 96%
Answer 11 : C) 92%
Explanation : The formula for finding process cycle efficiency is: Total value-added time / total cycle time. In this question, the value-added time is 2 hours, and the total cycle time is 2 minutes + 8 minutes + 120 minutes = 130 minutes. So the correct answer is 120 / 130 = 92%.
Exam mark breakdown

Leave a Reply
You must be logged in to post a comment.